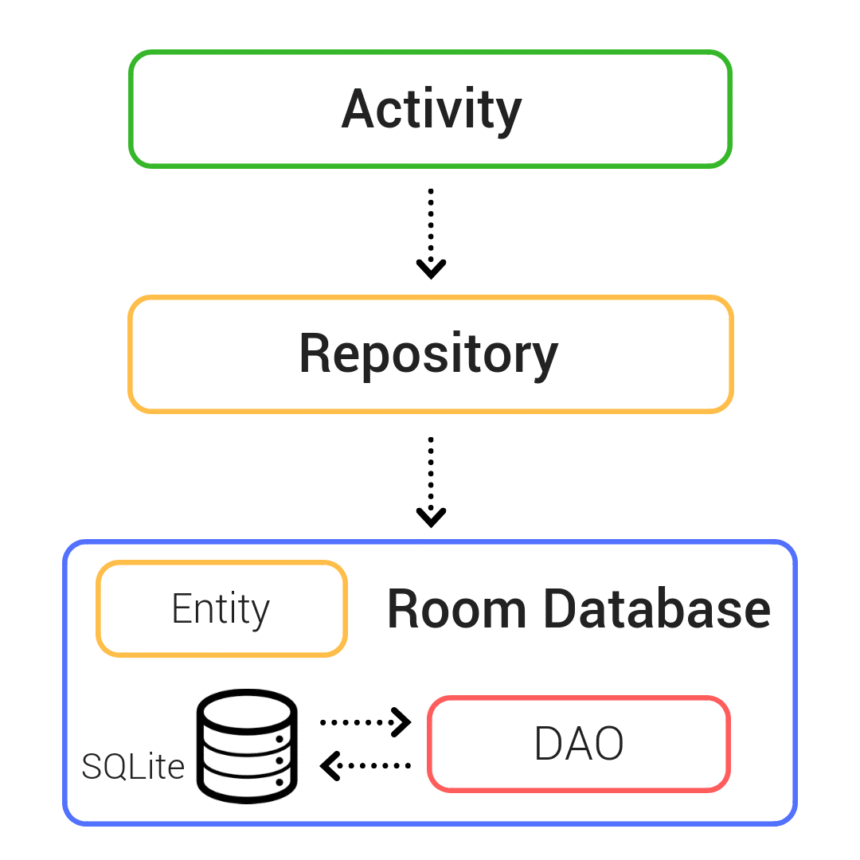
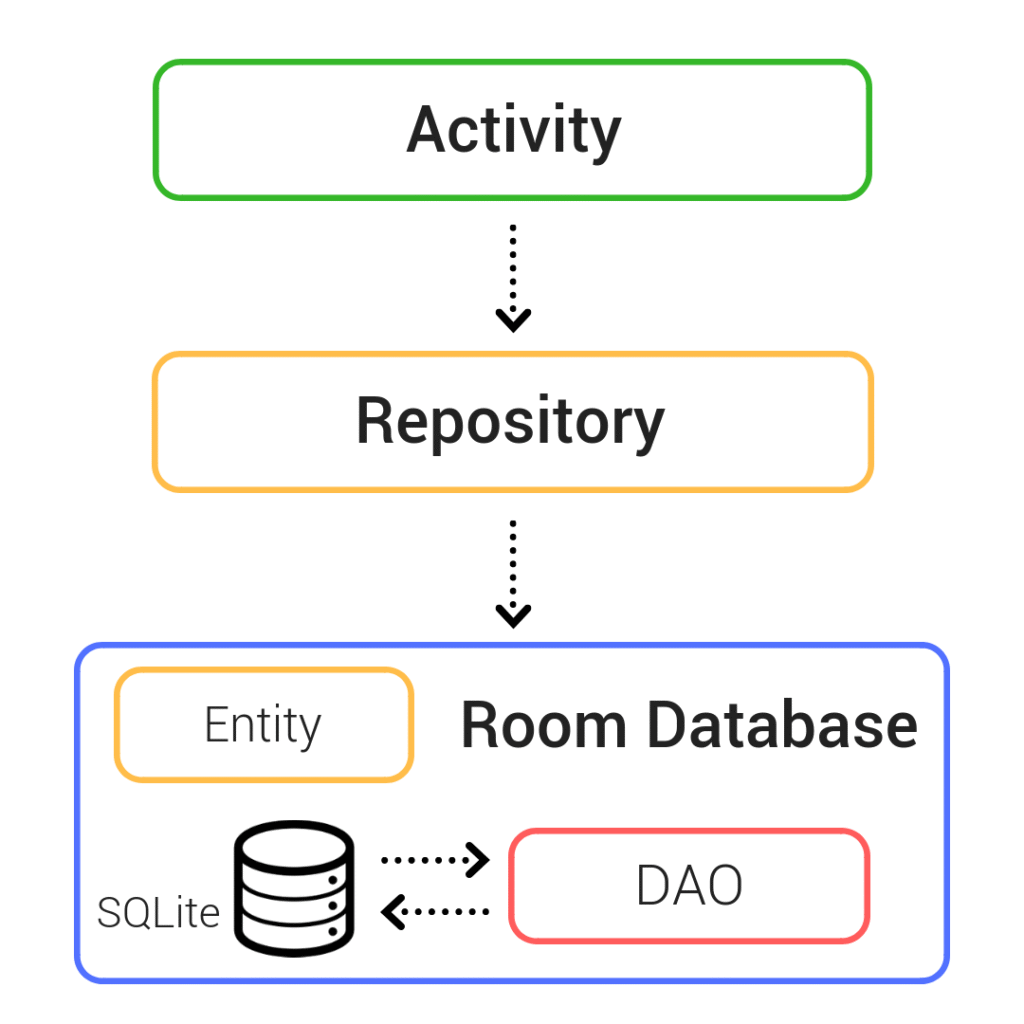
1. Tạo Entity
Ví dụ về một Note Entity:
@Entity(tableName = "notes")
public class Note {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
private int id;
@NonNull
@ColumnInfo(name = "title")
private String title;
@ColumnInfo(name = "content")
private String content;
@ColumnInfo(name = "timestamp")
private String timestamp;
public Note(String title, String content, String timestamp) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
@Ignore
public Note() {}
// Getters và setters...
}@Entity: đánh dấu class là một bảng trong cơ sở dữ liệu.
@PrimaryKey: khóa chính của bảng.
@ColumnInfo: chỉ định tên cột.
@Ignore: bỏ qua constructor không mong muốn.
2. DAO (Data Access Object)
@Dao
public interface NoteDao {
@Insert
long[] insertNotes(Note... notes);
@Query("SELECT * FROM notes")
LiveData<List<Note>> getNotes();
@Delete
int delete(Note... notes);
@Update
int updateNotes(Note... notes);
}@Insert, @Delete, @Update: các annotation tiện ích.
@Query: dùng để viết các câu SQL tùy chỉnh.
LiveData: tự động cập nhật khi dữ liệu thay đổi.
3. Room Database
@Database(entities = {Note.class}, version = 1)
public abstract class NoteDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
public static final String DATABASE_NAME = "notes_db";
private static NoteDatabase instance;
static NoteDatabase getInstance(final Context context) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = Room.databaseBuilder(
context.getApplicationContext(),
NoteDatabase.class,
DATABASE_NAME
).build();
}
return instance;
}
public abstract NoteDao getNoteDao();
}Sử dụng Singleton để đảm bảo chỉ có một instance cơ sở dữ liệu trong toàn bộ ứng dụng.
4. AsyncTasks cho các thao tác nền
Room không cho phép thực hiện truy vấn trực tiếp trên Main Thread. Do đó, bạn cần chạy các thao tác này trong background:
Thêm dữ liệu:
public class InsertAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<Note, Void, Void> {
private NoteDao mNoteDao;
public InsertAsyncTask(NoteDao dao) {
mNoteDao = dao;
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Note... notes) {
mNoteDao.insertNotes(notes);
return null;
}
}
Tương tự bạn có thể tạo UpdateAsyncTask và DeleteAsyncTask.
Truy xuất dữ liệu không cần AsyncTask vì đã dùng LiveData:
noteRepository.retrieveNotesTask().observe(this, new Observer<List<Note>>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(@Nullable List<Note> notes) {
// Dữ liệu đã cập nhật
}
});
Repository
public class NoteRepository {
private NoteDao noteDao;
private LiveData<List<Note>> notes;
public NoteRepository(Context context) {
NoteDatabase db = NoteDatabase.getInstance(context);
noteDao = db.getNoteDao();
notes = noteDao.getNotes();
}
public void insert(Note note) {
new InsertAsyncTask(noteDao).execute(note);
}
public void update(Note note) {
new UpdateAsyncTask(noteDao).execute(note);
}
public void delete(Note note) {
new DeleteAsyncTask(noteDao).execute(note);
}
public LiveData<List<Note>> retrieveNotesTask() {
return notes;
}
}
Có thể xem lại bài viết này: https://tinhoc123.edu.vn/lap-trinh/lap-trinh-android-java/tich-hop-room-voi-livedata-va-viewmodel-trong-android/